This is an example of Correspondence analysis by R.
It is in Analysis of similarity between items in rows and columns by R.
This is an example of Multiple correspondence analysis.
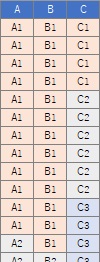
In this example, it is assumed that the folder "Rtest" on the C drive contains the data that is a contingency table with the name "Data.csv".

library(dummies)
library(MASS)
setwd("C:/Rtest")
Data <- read.csv("Data.csv", header=T)
Data_dmy <- dummy.data.frame(Data)
pc <- corresp(Data_dmy,nf=min(ncol(Data_dmy)))
pc1 <- pc$cscore
pc1 <- transform(pc1 ,name1 = rownames(pc1))
round(pc$cor^2/sum(pc$cor^2),2)# Calculate the contribution rate.
 Å@
Å@
In the above example, the 7th and subsequent eigenvalues ??have a low contribution rate, so we will exclude them from the subsequent analysis.
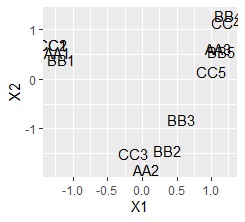
A multidimensional scatter plot is a scatter plot that allows you to see multiple dimensions in two dimensions. It is equivalent to the AB type multidimensional simultaneous attachment diagram . Starting with qualitative data eliminates the need for a procedure to combine both row-side and column-side calculation results.
MaxN = 6# Specify the number of unique values to use
Data11 <- pc1[,1:MaxN]
Data11_dist <- dist(Data11)
sn <- sammon(Data11_dist)
output <- sn$points
Data2 <- cbind(output, pc1)Å@
library(ggplot2)
ggplot(Data2, aes(x=Data2[,1], y=Data2[,2],label=name1)) + geom_text()
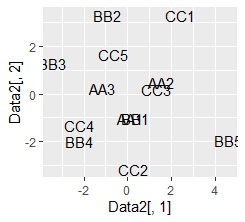
By the way, if you make a graph with the first and second components of correspondence analysis, it will be as follows, and it is not possible to separate.
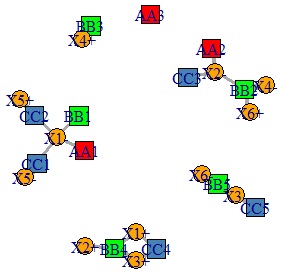
There is one more place to set the color, but the method of making is basically the same to the bipartite graphs.
MaxN = 6
library(igraph)# specifies the number of eigenvalues to use
library(sigmoid)
Data1p = pc1[,1:MaxN]
names(Data1p) = paste(names(Data1p),"+",sep="")
DM.matp = apply(Data1p,c(1,2),relu)
Data1m = -pc1[,1:MaxN]
names(Data1m) = paste(names(Data1m),"-",sep="")
DM.matm = apply(Data1m,c(1,2),relu)
DM.mat =cbind(DM.matp,DM.matm)
DM.mat <- DM.mat / max(DM.mat) * 10
DM.mat[DM.mat < 3] <- 0
DM.g<-graph_from_incidence_matrix(DM.mat,weighted=T)
V(DM.g)$color <- c("steel blue", "orange")[V(DM.g)$type+1]
V(DM.g)$color[1:3] <- "red"
V(DM.g)$color[4:8] <- "green"
V(DM.g)$shape <- c("square", "circle")[V(DM.g)$type+1]
plot(DM.g, edge.width=E(DM.g)$weight)